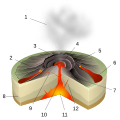
Portal:Volcanoes
The Volcanoes portal

On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 kilometers (1,900 mi) deep within Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
Large eruptions can affect atmospheric temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the Sun and cool Earth's troposphere. Historically, large volcanic eruptions have been followed by volcanic winters which have caused catastrophic famines.
Other planets besides Earth have volcanoes. For example, volcanoes are very numerous on Venus. In 2009, a paper was published suggesting a new definition for the word ‘volcano’ that includes processes such as cryovolcanism. It suggested that a volcano be defined as ‘an opening on a planet or moon’s surface from which magma, as defined for that body, and/or magmatic gas is erupted.’
This article mainly covers volcanoes on Earth. See § Volcanoes on other celestial bodies and Cryovolcano for more information. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The Armero tragedy (Spanish: Tragedia de Armero [tɾaˈxeðja ðe aɾˈmeɾo]) occurred following the eruption of the Nevado del Ruiz stratovolcano in Tolima, Colombia, on November 13, 1985. The volcano's eruption after 69 years of dormancy caught nearby towns unprepared, even though volcanological organizations had warned the government to evacuate the area after they detected volcanic activity two months earlier.
As pyroclastic flows erupted from the volcano's crater, they melted the mountain's glaciers, sending four enormous lahars (volcanically induced mudflows, landslides, and debris flows) down its slopes at 50 km/h (30 mph). The lahars picked up speed in gullies and engulfed the town of Armero, killing more than 20,000 of its almost 29,000 inhabitants. Casualties in other towns, particularly Chinchiná, brought the overall death toll to 23,000. Footage and photographs of Omayra Sánchez, a young victim of the disaster, were published around the world. Other photographs of the lahars and the impact of the disaster captured attention worldwide and led to controversy over the degree to which the Colombian government was responsible for the disaster. A banner at a mass funeral in Ibagué read, "The volcano didn't kill 22,000 people. The government killed them." (Full article...)Did you know
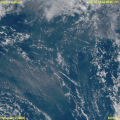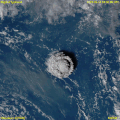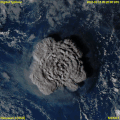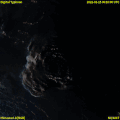
- ... that the volcanic chain (pictured) responsible for creating the island of Hawaii extends all the way to the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench, at the border of Russia?
- ... that Nintoku Seamount, an underwater volcano in the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, is over 56.2 million years old?
- ... that volcanoes in the Puyehue Volcano complex may have produced some of the most primitive magmas in the Andes?
- ... that Pilot Rock is one of the oldest volcanic formations in the Cascade Range?
- ... that one of a series of hotels called the Volcano House, built at the edge of Kīlauea volcano since 1846, burned to the ground from a kitchen fire?
- ... that the eruption of Amak Volcano in about 2550 BCE was confirmed by tephrochronology?
- ... that the Bobrof Volcano is an uninhabited island in the Andreanof Islands, part of Alaska's Aleutian archipelago?
- ... that the closest transportation to Davidof Volcano is 199 miles (320 km) away in Adak, Alaska?
General images
Selected biography -
Berend George Escher (4 April 1885 – 11 October 1967) was a Dutch geologist.
Escher had a broad interest, but his research was mainly on crystallography, mineralogy and volcanology. He was a pioneer in experimental geology. He was a half-brother of the artist M. C. Escher, and had some influence on his work due to his knowledge of crystallography. M.C. Escher created a woodcut ex libris for his brother 'Beer' with a stylized image of a volcano around 1922 (Bool number 91).
Escher was the son of the civil engineer G. A. Escher, a director of the Dutch watermanagement (Rijkswaterstaat) and his first wife, Charlotte Marie Hartitzsch. Escher spent his youth in Switzerland. He studied geology at the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (Technical University) of Zürich, where he was a pupil of Albert Heim. He finished his studies in 1911 and returned to the Netherlands where he first became the assistant of M. E. F. T. Dubois at the University of Amsterdam and then curator of the geological collections at Delft University. In 1916 he was employed by Royal Dutch Shell in the Dutch East Indies. (Full article...)Selected picture
 |
Puʻu ʻŌʻō is a cinder/spatter cone in the eastern rift zone of the Kīlauea volcano of the Hawaiian Islands. Puʻu ʻŌʻō has been erupting continuously since January 3, 1983, making it the longest-lived rift-zone eruption of the last two centuries. From 1983 through 1998, lava from Puʻu ʻŌʻō covered more than 97 km² (37 square miles).
Selected quote
"El enemigo sigue ahí. (The enemy is still there)"
— Sergio Galilea, intendant of the Los Lagos Region, Chile, speaking of the Chaitén Volcano on the first anniversary of its eruption, 2 May 2009
Related portals
WikiProjects
Volcanoes topics
Subcategories
Featured work and other approved content

Featured articles: 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens • 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes • Amchitka • Armero tragedy • Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve • Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) • David A. Johnston • Enceladus (moon) • Geology of the Lassen volcanic area • Io (moon) • Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount • Mauna Kea • Mauna Loa • Metacomet Ridge • Mono-Inyo Craters • Mount Cayley volcanic field • Mount St. Helens • Mount Tambora • Nevado del Ruiz • Surtsey • The Volcano (British Columbia) • Triton (moon) • Upper and Lower Table Rock • Volcanism on Io • Volcano (South Park) • Yellowstone National Park
Featured lists: List of volcanoes in Indonesia • List of volcanoes in the Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain • List of largest volcanic eruptions
Featured pictures: There are currently 43 volcano-related Featured pictures. A full gallery can be seen here.

Good articles: Abyssal plain • Amak Volcano • Anahim hotspot • Axial Seamount • Ben Nevis • Bowie Seamount • Crater Lake • Davidson Seamount • Ferdinandea • Gareloi Volcano • Geyser • Glacier Peak • Hawaii hotspot • Hualālai • Kohala (mountain) • Lake Toba • Minoan eruption • Mount Adams (Washington) • Mount Bailey • Mount Baker • Mount Cleveland (Alaska) • Mount Edziza volcanic complex • Mount Garibaldi • Mount Hood • Mount Kenya • Mount Rainier • Mount Redoubt • Mount Tehama • Mount Thielsen • Mount Vesuvius • Peter I Island • Roxy Ann Peak • Rùm • Sakurajima • Sangay • Silverthrone Caldera • Staffa • Types of volcanic eruptions • Volcanic ash • Weh Island • Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field • Yamsay Mountain
Valued pictures: A gallery of volcano-related valued pictures can be seen here.
What you can do

- Add the {{WikiProject Volcanoes}} message box to talk pages of articles within the scope of this project, including appropriate assessments, if needed.
- Add appropriate volcano type categories to articles, and verify the accuracy of any existing categories. See the section "Categorization" below.
- Add {{infobox mountain}} to articles if needed and missing, and add volcano-related fields to existing infoboxes if these are missing.
- Expand volcano articles which are stubs, especially by adding photos and (most importantly) proper references.
- Help improve articles related to Hawaiian and Canadian volcanism by joining the Hawaiian and Canadian workgroups.
- Improve some of the project's most visible articles.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus